Bay of Plenty demographics Governance and management Hazard management
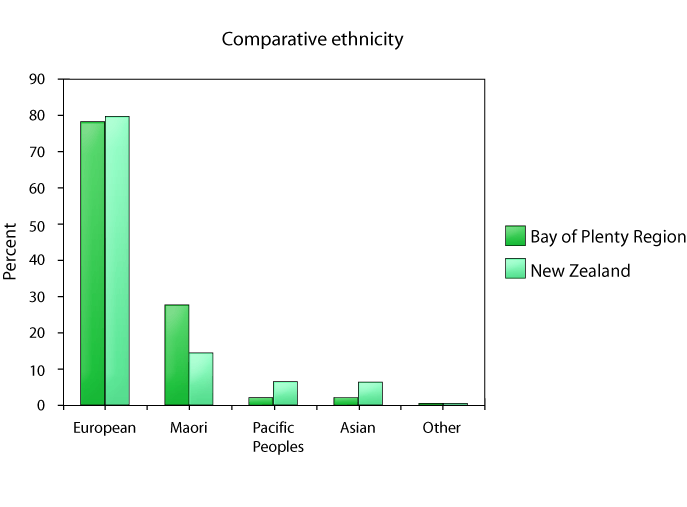
In the 2001 nationwide census, the Bay of Plenty regional population was about 240,000. The majority of people were in the 15-64 age bracket, with those older than 65 making up a slightly higher proportion than the national average (see the graph below). The ethnic composition of the region is dominantly of European descent, but also includes a Maori population that exceeds the national average. Projected population growth for the region is estimated at 28% by 2026, slightly above most other regions in the country. More than two-thirds (68%) live in the main urban centres of Tauranga, Rotorua, and Whakatane.
Move the slider to the right to see how suburban development at Ohope has now fully occupied the narrow coastal strip, placing these homes at risk of inundation during storms and tsunami.
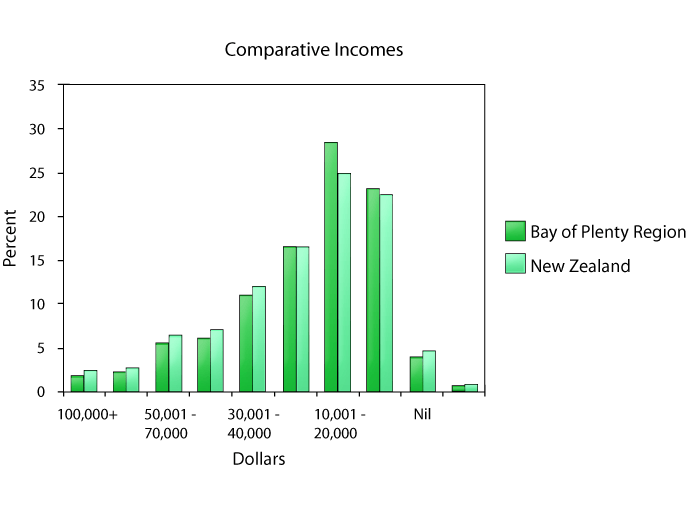
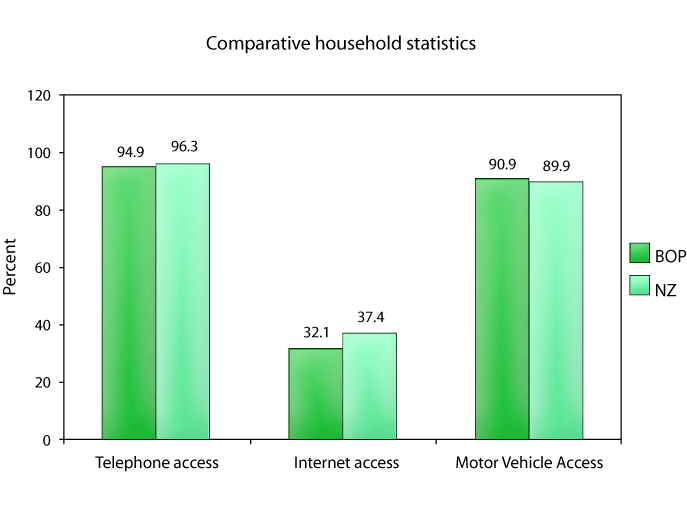
Some other key points from the 2001 census are:
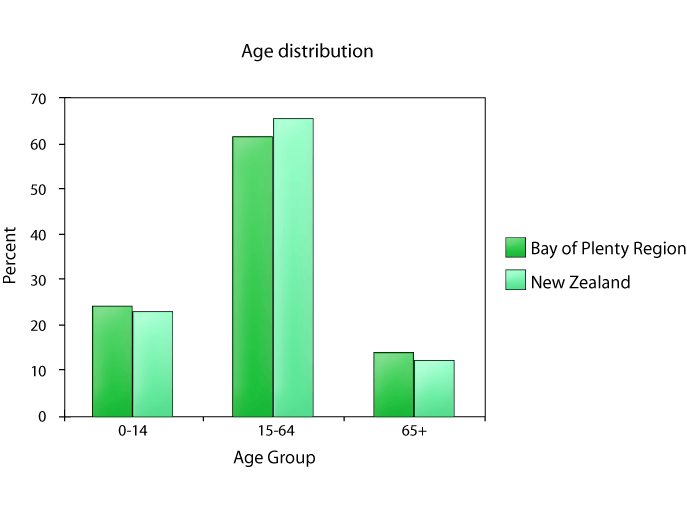
The region is administered by Environment Bay of Plenty (regional council), while local issues are handled by the seven district councils; Tauranga, Western Bay of Plenty, Rotorua, Whakatane, Kawerau, Opotiki, and Taupo (in part). Go to the interactive map to see the council borders. The responsibilities of the respective councils are as follows:
The role of a regional council is to manage the natural resources, environmental planning and all regulations administered at a regional level. The functions of the territorial authorities (district councils) is to provide local services such as water, rubbish collection and disposal, sewage treatment, parks, reserves, street lighting, roads and libraries. They process building and environmental consents and administer other regulatory tasks.
(courtesy http://www.govt.nz/record?recordid=1921)
Regional and district councils are responsible for hazard assessment and prevention in their respective areas. This includes assessing risks and adjusting local response plans to national guidelines and plans as administered by the Ministry of Civil Defence and Emergency Management, and the legislative direction of the Civil Defence Emergency Management Act 2002. In the Bay of Plenty, this is coordinated by the Bay of Plenty Emergency Management Group (as a part of Environment Bay of Plenty located on the river front in Whakatane), who with the district councils, assess risk and adjust plans and management respectively. For example, in coastal districts (as opposed to those inland) tsunami are a risk and response plans and management are adjusted accordingly.