Anatomy & Physiology
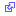
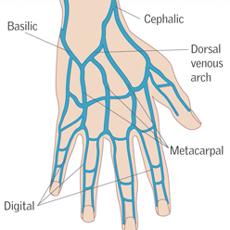
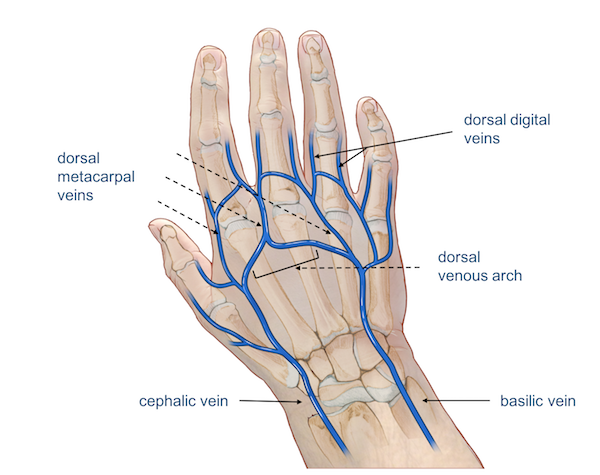
DigitalVeins
- Located on fingers
- Suitable for small size cannulae 22-24g
- Because of small size and location, it is used as a last resort.
https://journals.rcni.com/nursing-standard/vascular-access-a-guide-to-peripheral-venous-cannulation-ns2005.08.19.49.48.c3935
Metacarpal Veins
- Located on top of the hand
- Suitable for 18-24g cannulae
- Easy to see and feel
- Increased risk of infiltration & phlebitis
https://www.pinterest.nz/pin/291959988343495045/
Metabrachial Veins
- Located under wrist
- Only for 20-24g cannulae
- Easy to see
- Very painful to access.
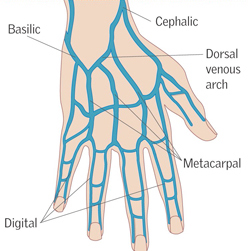
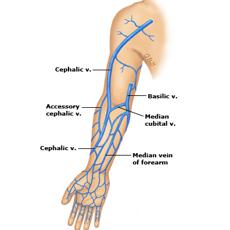
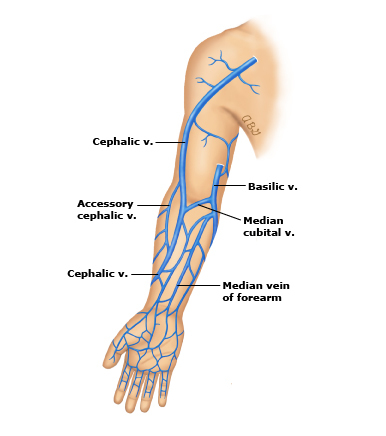
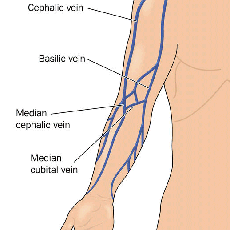
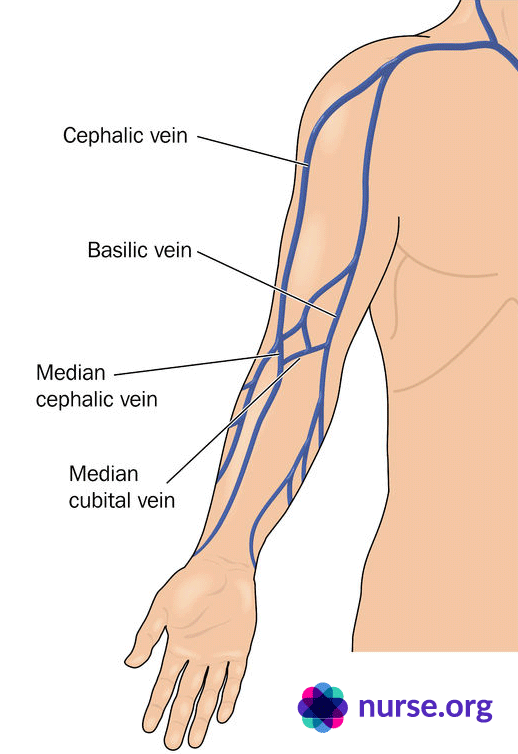
Cephalic Vein
- Runs from wrist to shoulder.
- Suitable for 16-24g cannulae
- Large vein proximally
- Suitable for most solutions, medications & transfusions
https://pbrainmd.wordpress.com/2017/07/27/upper-extremity-veins/
Basilic Vein
- Runs on the medial aspect of the arm
- Suitable for 16-24g cannulae
- Suitable for most solutions, medications and infusions.
- Can roll easily.
https://pbrainmd.wordpress.com/2017/07/27/upper-extremity-veins/
Anticubital Veins
Refers to veins which pass through the antecubital fossa:
- basilic,
- cephalic and
- median cubital vein
- Usually reserved for blood drawing, PICC’s & emergencies.
- Elbow area shortens catheter life.
https://nurse.org/articles/how-nurses-professionally-draw-blood/
Arteries
- When palpated, arteries pulsate (but not always)
- Arteries blanche when flushed
- Arteries have bright red blood
- It is difficult to distinguish arteries and veins in an infant’s scalp

|
Arteries vs Veins
|