When to examine a baby
- Immediately after birth
- Prior to discharge
- Whenever there is concern
The Blue Card
PAGE 2 OF THE BLUE CARD WILL OUTLINE THE AREAS THAT NEED COVERING-this is the card that is used at National women's hospital -check at your cohort to see if their card is the same.
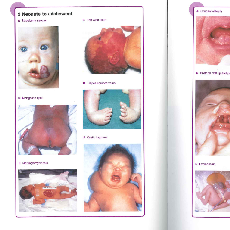
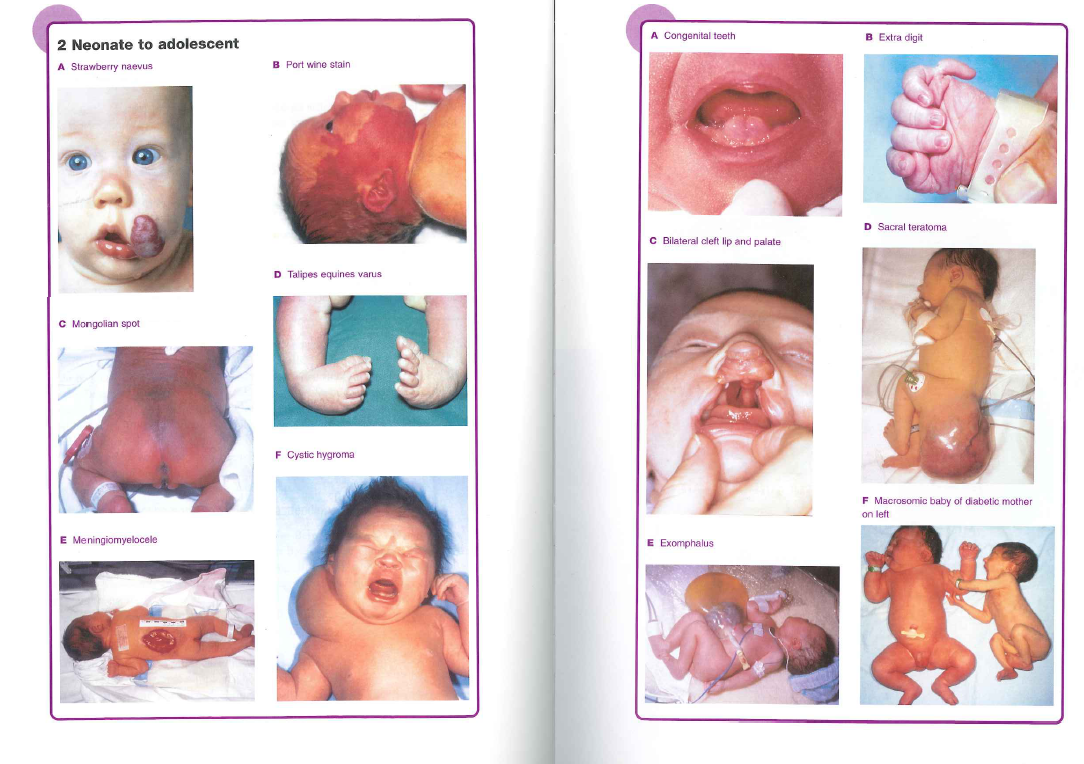
Where possible you should try to examine the baby with the parents present and it is important to give them a true account of the baby's physical state. Examination at birth will establish a baseline. Close examination will detect any abnormalities and if found will require the baby to be appropriately referred for treatment to minimise morbidity. Here are some abnormalities that you may encounter.
General examination points
- Measurements: weight, length and head circumference, plot
- Overall inspection, including dysmorphism
- Respiratory and heart rates
- Activity levels, colour, fetal malnutrition, post dates
Detailed examination points
Head - anterior & posterior fontanelles, sutures
- Face - eyes for red reflex, coloboma, epicanthic folds, nose, choanal atresia, ears-shape and placement, mouth-fully inspect with light
- Neck - sternomastoid muscles, rotation of head
- Chest
- Asymmetry, thoracic cage defects and spinal scoliosis
-Apex beat
- Auscultation of lungs and heart (CXR if required)
- Abdomen
-Scaphoid (?CDH) or distended
-Palpate for liver, spleen and kidneys, other masses
-Cord-omphalocoele, hernia
-Femoral pulses
-Inguinal hernia
You have already looked at some abnormalities -here is a list with some others that you need to be checking for:
- Genitalia - Ambiguous genitalia (CAH), hypospadias
- Anus: Imperforate anus
- Hips - Developmenatal disclocation (dyspasia) o f the hip-DDH.
You will need to learn how to do Barlow's and Ortolani tests
- Feet -Talipes equinovarus and calcaneo valgus
- Nervous System -Activity levels, tone, reflexes
- Back -Myelomeningocoele, lipomas, midline lesions
Edit page