Literature reviews 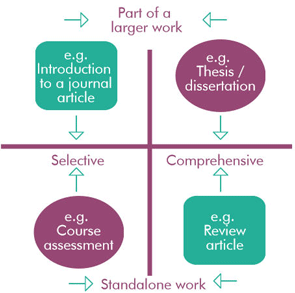
A literature review is either a standalone piece of research or part of a larger work.
Standalone published works are variously titled or subtitled literature review, narrative review, integrative review or systematic literature review.
A literature review or a systematic literature review is not the same as a systematic review, though some aspects of the systematic process maybe shared between a systematic literature review and a systematic review.
There is no one way to write and structure a literature review as they do tend to be discipline specific.
If you are writing a literature review as part of an Honours or Masters dissertation or thesis, talk with your supervisor to find out about accepted formats or conventions.
Find some literature reviews similar to your topic or field of study to see their structure and the way they are written.
- For Honours and Masters dissertations ask your supervisor as copies of previous dissertations are kept in departments or schools.
- For examples of Masters and Doctoral theses check the Finding theses and dissertations webpage.
- For articles use databases such as Google Scholar, Embase, Scopus, CINAHL and APA PsycINFO and search for literature review or narrative review in the title. Some databases also have literature review or review as part of their 'Limits' to add to your search.
If you are interested:
Jones, A. "Ask the professor" about... Good literature reviews. MAI Review, 2007, 1, Writing Workshop 2.
Gregory, A. T. and A. R. Denniss (2018). An introduction to writing narrative and systematic reviews - Tasks, tips and traps for aspiring authors. Heart Lung Circ 27(7): 893-898. 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.03.027.
Ferrari R. Writing narrative style literature reviews. Medical Writing. 2015 Dec 1;24(4):230-5.
Focused on clinical research
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Computational Biology. 2013 Jul 18;9(7):e1003149.
Baethge, C., et al. (2019). SANRA-a scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res Integr Peer Rev 4: 5. 10.1186/s41073-019-0064-8.
Image source: Monash University Library. Researching for your literature review. 1: Literature reviews
| Postgraduate Research Skills Look at Postgraduate research skills at Te Tumu Herenga Work though the module: Literature review: Organising and writing |
 Your literature review topic: Searching for information.
Your literature review topic: Searching for information.
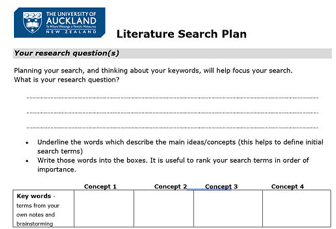
If you are doing a literature review for an assessment or as part of your research you may find the Literature Search Plan useful.
- Download the Literature Search Plan.
- Refer when needed to some of the other appropriate modules in Information Skills Online (chose from the left side menu)
- Depending on your topic, some of the main databases to use are Google Scholar, Medline (Ovid), Embase, Scopus or CINAHL.
There are a series of short videos on how to search Medline.
![]()
Literature Review Search Worksheet.docx
Literature Search Plan
A useful resource for undergraduate students enrolled in MedSci courses:
| Researching and writing a literature review in the biomedical sciences |
|
Additional easy to read information is in...
| Aveyard H. Doing a literature review in health and social care: A practical guide. 4th ed. London: Open University Press, McGraw-Hill Education; 2019. Note there are previous editions including the 3rd as an e-book. |
 | Aveyard H, Payne S, Preston NJ. A post-graduate's guide to doing a literature review in health and social care. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2016. |
 | Booth A, Sutton A, Papaioannou D. Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. 2nd ed. Los Angeles: Sage; 2016 'Showing you how to take a structured and organized approach to a wide range of literature review types, this book helps you to choose which approach is right for your research. Packed with constructive tools, examples, case studies and hands-on exercises, the book covers the full range of literature review techniques.' There is a companion website. |
See also:
'read over other guides to writing literature reviews so that you see different perspectives and approaches'1
|
|
1. Helen Mongan-Rallis. Guidelines for writing a literature review. http://www.duluth.umn.edu/~hrallis/guides/researching/litreview.html
Edit page