Pre Course Test
ACLS PRE-COURSE MCQ TEST
Choose one option that best answers the question-1800x2400_px_pp.jpg)
Dr. Magdi Moharib;
M.B., B.S., M.Anaesth/IC, MD, PGDipClinEd
1. A 65-year-old man collapses in the medical word, CPR started for the first time after 5 minutes delay. The defibrillator monitor shows fine (low-amplitude) VF.
A 65-year-old man collapses in the medical word, CPR started for the first time after 5 minutes delay. The defibrillator monitor shows fine (low-amplitude) VF.
Which actions should be taken next?
2.
A cardiac arrest patient with CPR in progress arrives in the ED with PEA of heart rate of 40/min. ET tube placement is confirmed, and IO access is established.
Which medication is most appropriate to give next?
3.
Which of the following statements are possible positions of the defibrillation pads on this patient?
One pad to the right of upper sternum below the right clavicle and the other in mid axillary line at level of V6
One pad anterior to left precordium and the other inferior to left scapula (antero-posterior)
One pad in mid axillary line at level of V6 and the other over the right scapula (Postero-lateral)
Bi-axillary on either side at midaxillary line
4. Which action is performed as you prepare for defibrillator discharge?
Which action is performed as you prepare for defibrillator discharge?

5. A woman with a history of narrow-complex SVT arrives in the ED. She is alert and oriented but pale. Heart rate is 165/min, and the ECG shows SVT. Blood pressure is 105/70 mm Hg. IV access has been established. Which is the most appropriate initial treatment?
A woman with a history of narrow-complex SVT arrives in the ED. She is alert and oriented but pale. Heart rate is 165/min, and the ECG shows SVT. Blood pressure is 105/70 mm Hg. IV access has been established. Which is the most appropriate initial treatment?
6.
What is a common undesirable action during cardio-pulmonary arrest management?
7. The ED Registrar attempted endotracheal intubation for a patient in Cardio-pulmonary arrest. While performing positive-pressure ventilation with BVM, auscultation reveals gurgling over the epigastrium but no breath sounds. Waveform capnography is zero or flat.
The ED Registrar attempted endotracheal intubation for a patient in Cardio-pulmonary arrest. While performing positive-pressure ventilation with BVM, auscultation reveals gurgling over the epigastrium but no breath sounds. Waveform capnography is zero or flat.
Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
8.
Which statement about IV administration of medications during CPR is true?
9.
A 75-year-old man with IHD with recurrent VF now has a wide-complex rhythm with no pulse. 1 mg IV adrenaline administered after a second shock. Now a third shock is given.
Which drug is most appropriate to give next?
10.
Which cause of PEA is most likely to respond to immediate treatment?
11.
Which drug-dose combination is recommended as the initial medication for a patient in asystole?
12. 48 years-old patient with a heart rate of 30/min reports with chest pain. He is confused with oxygen saturation is 89% on room air.
48 years-old patient with a heart rate of 30/min reports with chest pain. He is confused with oxygen saturation is 89% on room air.
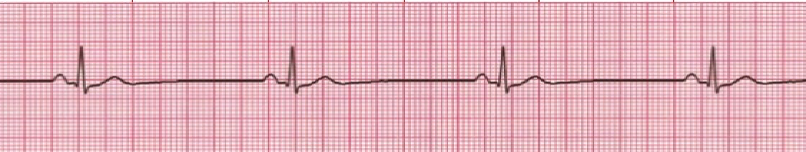
After oxygen administration, what is the appropriate drug you should administer to this patient?
13. Which statement correctly describes the ventilation during CPR in an adult victim that should be provided after an advanced airway insertion (ETT / LMA)?
Which statement correctly describes the ventilation during CPR in an adult victim that should be provided after an advanced airway insertion (ETT / LMA)?
14.
A patient in the ED reports 30 minutes of severe, crushing, substernal chest pain. Vitals are:
Blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg,
Heart rate 55/min,
Monitor shows regular sinus bradycardia.
The patient has received aspirin 325 mg orally, oxygen 4 L/min via nasal prongs, and 3 sublingual nitroglycerin sprays 5 minutes apart, but he continues to have nausea and severe pain.
Which agent should be given next if there are no contraindications?
15. A 70-year-old hypertensive male who is profusely diaphoretic reports to ED with crushing chest pain and severe shortness of breath. He chewed one aspirin tablet at home and is now receiving oxygen.
A 70-year-old hypertensive male who is profusely diaphoretic reports to ED with crushing chest pain and severe shortness of breath. He chewed one aspirin tablet at home and is now receiving oxygen.
Which treatment sequences are most appropriate at this time?
16. A 50-year-old man has a >2mm ST elevation in leads V2-V4. Pain has been relieved with sublingual nitroglycerin. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, and heart rate is 59/min.
A 50-year-old man has a >2mm ST elevation in leads V2-V4. Pain has been relieved with sublingual nitroglycerin. Blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, and heart rate is 59/min.
Which treatment is most appropriate for this patient at this time?
17. A 70-year-old man at a shopping mall reports a moderate headache and trouble walking. He has a facial droop, slurred speech, and difficulty raising his right arm. He says that he takes “several medications” for high blood pressure.
A 70-year-old man at a shopping mall reports a moderate headache and trouble walking. He has a facial droop, slurred speech, and difficulty raising his right arm. He says that he takes “several medications” for high blood pressure.
Which action is most appropriate at this time?
18.
Which rhythm is a proper indication for transcutaneous pacing if atropine fails to work?
19.
Which cause of out-of-hospital asystole is most likely to respond to treatment?
20. lungs sounds are clear, and she reports no shortness of breath or dyspnea on exertion. The ECG monitor displays a regular narrow- complex tachycardia.
A 34-year-old woman with a history of rheumatic fever and mitral valve prolapse presents to the ED with palpitations. Her vital signs are as follows:
heart rate is 165/min,
respiratory rate is 14/min,
blood pressure is 118/92 mm Hg,
oxygen saturation is 98% on room air
lungs sounds are clear, and she reports no shortness of breath or dyspnea on exertion. The ECG monitor displays a regular narrow- complex tachycardia.
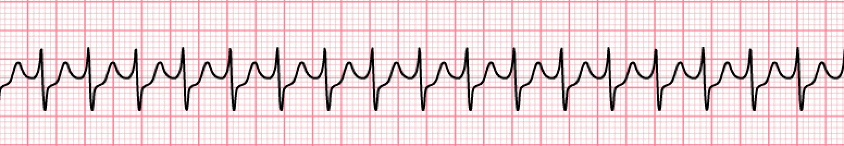
Which term best describes her condition?
21. A 75-year-old man presents to the ED with a history of light-headedness, palpitations, and mild exercise intolerance lasting 1 week.
A 75-year-old man presents to the ED with a history of light-headedness, palpitations, and mild exercise intolerance lasting 1 week.
The initial 12- lead ECG displays atrial fibrillation with a heart rate of 120 to 150/min and blood pressure of 90/65 mm Hg.
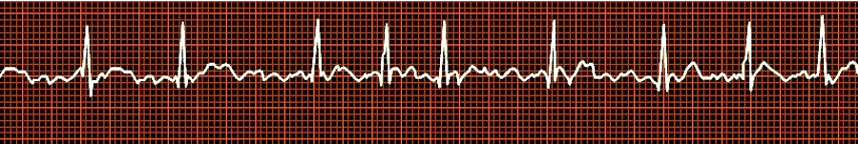
Which therapy is the most appropriate?
22.
Which agent is used frequently in the early management of acute coronary syndrome?
23.
You prepare for synchronized cardioversion for a 48-year-old woman with unstable tachycardia. The patient suddenly becomes unresponsive and pulseless as the rhythm changes to an irregular, chaotic, VF-like pattern. You charge to 200 J and press the SHOCK button, but the defibrillator does not deliver a shock.
Why?
24. Chest compressions and effective bag-mask ventilation are ongoing in a patient with cardiopulmonary arrest.
Chest compressions and effective bag-mask ventilation are ongoing in a patient with cardiopulmonary arrest.
The rhythm check reveals pulseless sinus bradycardia at a rate of 30/min.
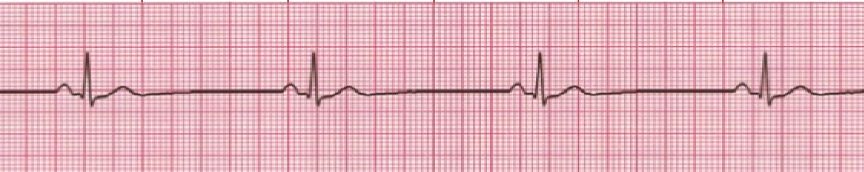
Which action should be done next?
25.
The following patients were diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke. Which of these patients might be a candidate for IV fibrinolytic therapy?
26.
A 25-year-old woman presents to the ED with another episode of palpitations. Her medical history includes an electrophysiological stimulation study (EPS) that confirmed a reentry tachycardia, no Wolff- Parkinson-White syndrome, and no pre-excitation. Heart rate is 180/min & BP 105/70mmHg.
The patient reports mild shortness of breath. Vagal maneuvers have no effect on heart rate or rhythm.
Which is the most appropriate next intervention?
27.
A patient with a heart rate of 30 to 40/min reports dizziness, cool and clammy extremities, and dyspnea. All treatment modalities are present. What would you do first?
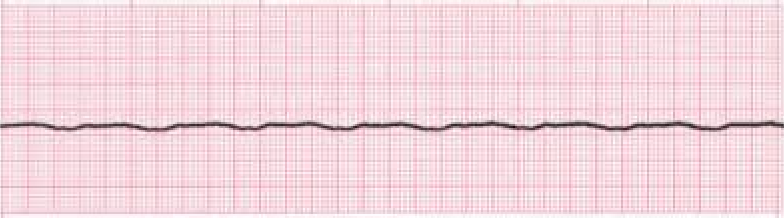
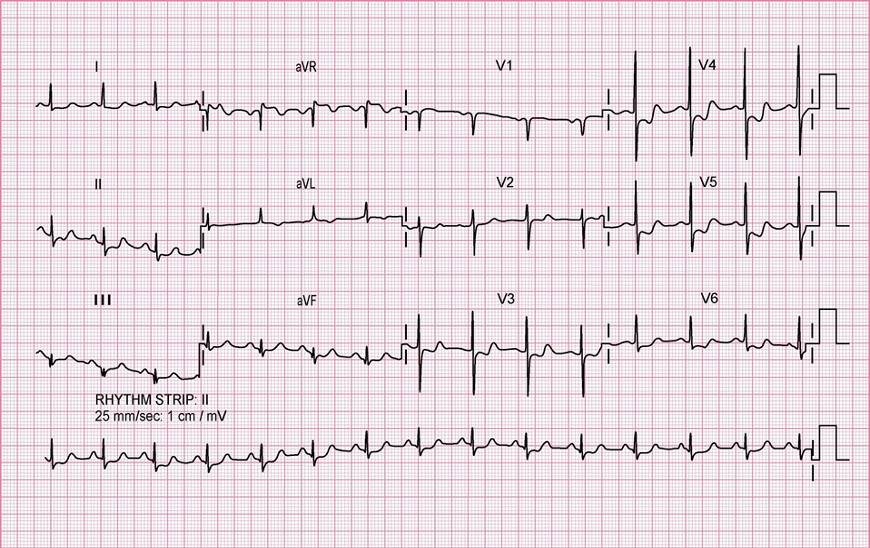
28. Comment on the rhythm
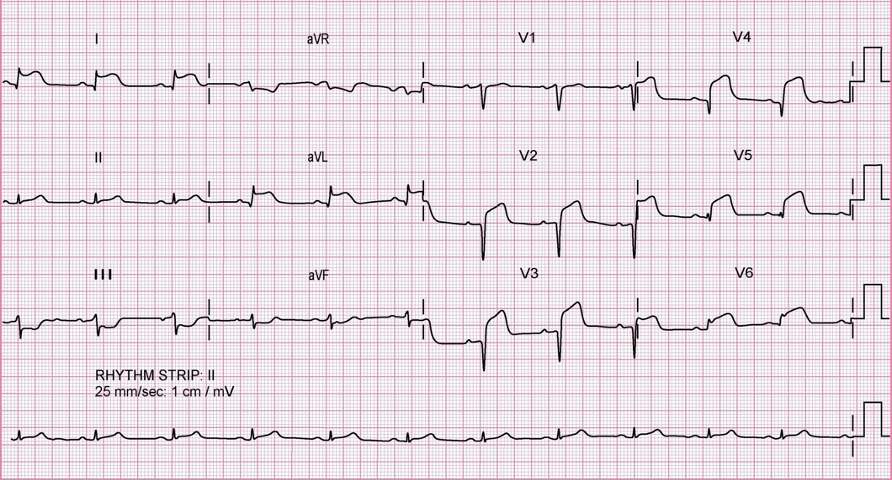

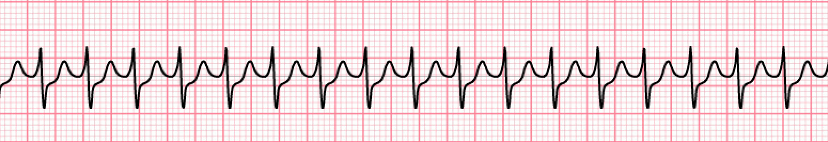
29. Comment on the rhythm

30. Which of the following options is the correct landmark for the insertion of a needle for an emergency needle decompression for tension pneumothorax?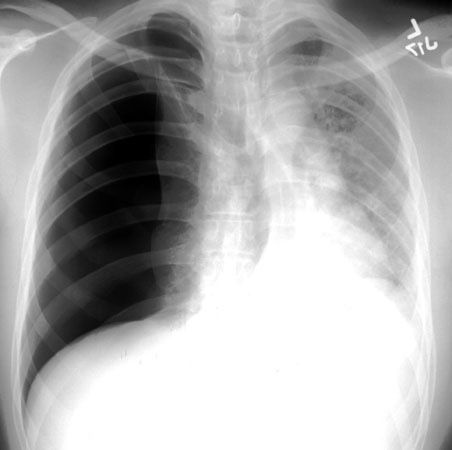

| « Feedback |