|
|

Narrowing a search: If you are getting too many results then try one of the following methods.
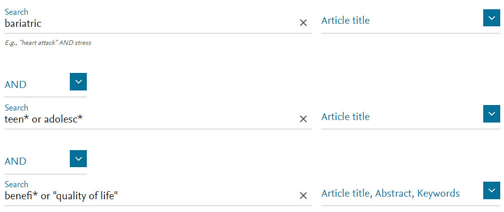
- Limit your search to a field
eg, title (ie article title). Example search in Scopus:
- Apply a narrower term to your search
eg, exercise therapy instead of exercise
myocardial infarction instead of cardiovascular disease
- Search for a phrase instead of two separate keywords (especially important in Scopus, Google, Google Scholar)
eg "autism spectrum" (use speech marks) instead of autism spectrum.
- Tick the 'Focus' box for the MeSH, CINAHL Heading, Emtree Heading, APA PsycINFO heading.
See Explode & focus.
- Add another concept to your search
eg, heart disease AND obesity AND nutrition instead of heart disease AND obesity.
- Remove any terms or words that broaden the scope of your topic
eg, if your topic is glaucoma remove eye disease (if you have included this) from your search.
- Limit your search by date
eg, last 2 or 5 years.
- Limit your search by language
eg, English.
- Limit your search by publication type
eg, randomized controlled trial, multicenter study, review.
- Limit your search by clinical query if appropriate
eg, therapy
- Limit your search by age group if appropriate.
- If you used truncation check you have truncated at the best place in a word eg nurs* will find nurse or nurses or nursing or nursery or nurseries. It might be best to spell out each appropriate word.
- Add an appropriate subheading if you are using MeSH in Medline (Ovid) or subject headings in CINAHL Plus.
|